Aws-Scale
AWS Scaling Made Simple.
Problem
Developing applications on AWS can get expensive. Leaving EC2s, DynamoDB tables, and Kinesis streams running in test accounts adds up. Complex cloud services rely on multiple resources that have to manually be scaled up. Once up, resources can be easily forgotten about and left at development or performance testing levels.
Solution
AWS-Scale is a simple library used to automate the scaling process. You can use it to build single lambda functions per app stack that automatically scale down resources every day. Then use aws-scale in a node script to scale the entire stack back up and notify you when complete.
Usage
To install: npm install aws-scale
Currently supported AWS resources:
- DynamoDB
- AutoScaling Groups
Below is an example Lambda function that scales down a test webservice:
var scale = require('aws-scale');
exports.handler = function (event, context, callback) {
// Data store for the webservice
var dynamoParams = {
TableName: 'userDataTable',
ProvisionedThroughput: {
ReadCapacityUnits: 1,
WriteCapacityUnits: 1
},
GlobalSecondaryIndexUpdates: [
{
Update: {
IndexName: 'lastLoginDate',
ProvisionedThroughput: {
ReadCapacityUnits: 1,
WriteCapacityUnits: 1
}
}
}
]
};
// AutoScale group containing EC2 instances responding to http requests
var asgParams = {
AutoScalingGroupName: 'expressWebServiceASG',
DesiredCapacity: 0
};
var resourceSet = new scale.ResourceSet();
resourceSet.add(new scale.DynamoDB(dynamoParams));
resourceSet.add(new scale.AutoScaleGroup(asgParams));
// Callback will be invoked after AWS responds to every scale request.
resourceSet.scale(function (err) {
if (err) {
// CloudWatch hides arrays, this will print the entire array out for debugging purposes.
callback(JSON.stringify(err));
} else {
callback();
}
});
};This allows you to schedule a single lambda function to scale down an entire application stack for the night.
A similar pattern can be followed for node scripts (or another scheduled Lambda)that scale the resources back up for development:
var scale = require('aws-scale');
var dynamoParams = {
TableName: 'userDataTable',
ProvisionedThroughput: {
ReadCapacityUnits: 500,
WriteCapacityUnits: 500
},
GlobalSecondaryIndexUpdates: [
{
Update: {
IndexName: 'lastLoginDate',
ProvisionedThroughput: {
ReadCapacityUnits: 100,
WriteCapacityUnits: 100
}
}
}
]
};
var asgParams = {
AutoScalingGroupName: 'expressWebServiceASG',
DesiredCapacity: 3
};
// Pass optional parameter object to poll scaling progress and notify you via console logs.
var resourceSet = new scale.ResourceSet({pollScaleProgress: true});
resourceSet.add(new scale.DynamoDB(dynamoParams));
resourceSet.add(new scale.AutoScaleGroup(asgParams));
// ResourceSet will start scaling operations via AWS SDK. It will then poll the resources every 5 seconds to check scaling status.
resourceSet.scale();The script can be run via node webServiceScaleUp.js.
Callback Return
The callback passed to resourceSet.scale is treated like an aws callback with an err and data parameter. If every resource successfully starts it's scale operation, an array of status objects will be returned as data with a null err parameter. If any of the scale attempts receive an error from AWS, the array of all resource statuses will be returned as an error.
Example successful return - callback (null, data):
data = [
{
type: 'DynamoDB',
name: 'userDataTable',
status: 'success'
},
{
type: 'AutoScaleGroup',
name: 'expressWebServiceASG',
status: 'success'
}
];Example error return - callback (err, null):
// Will wait for a response from all resources before returning array with error.
err = [
{
type: 'DynamoDB',
name: 'userDataTable',
status: 'failure',
error: { // Error object returned from AWS SDK call.
"errorMessage": "2 validation errors detected: Value '0' at 'provisionedThroughput.writeCapacityUnits' failed to satisfy constraint: Member must have value greater than or equal to 1; Value '0' at 'provisionedThroughput.readCapacityUnits' failed to satisfy constraint: Member must have value greater than or equal to 1",
"errorType": "ValidationException",
}
},
{
type: 'AutoScaleGroup',
name: 'expressWebServiceASG',
status: 'success'
}
];
Watch Scaling Status in Node
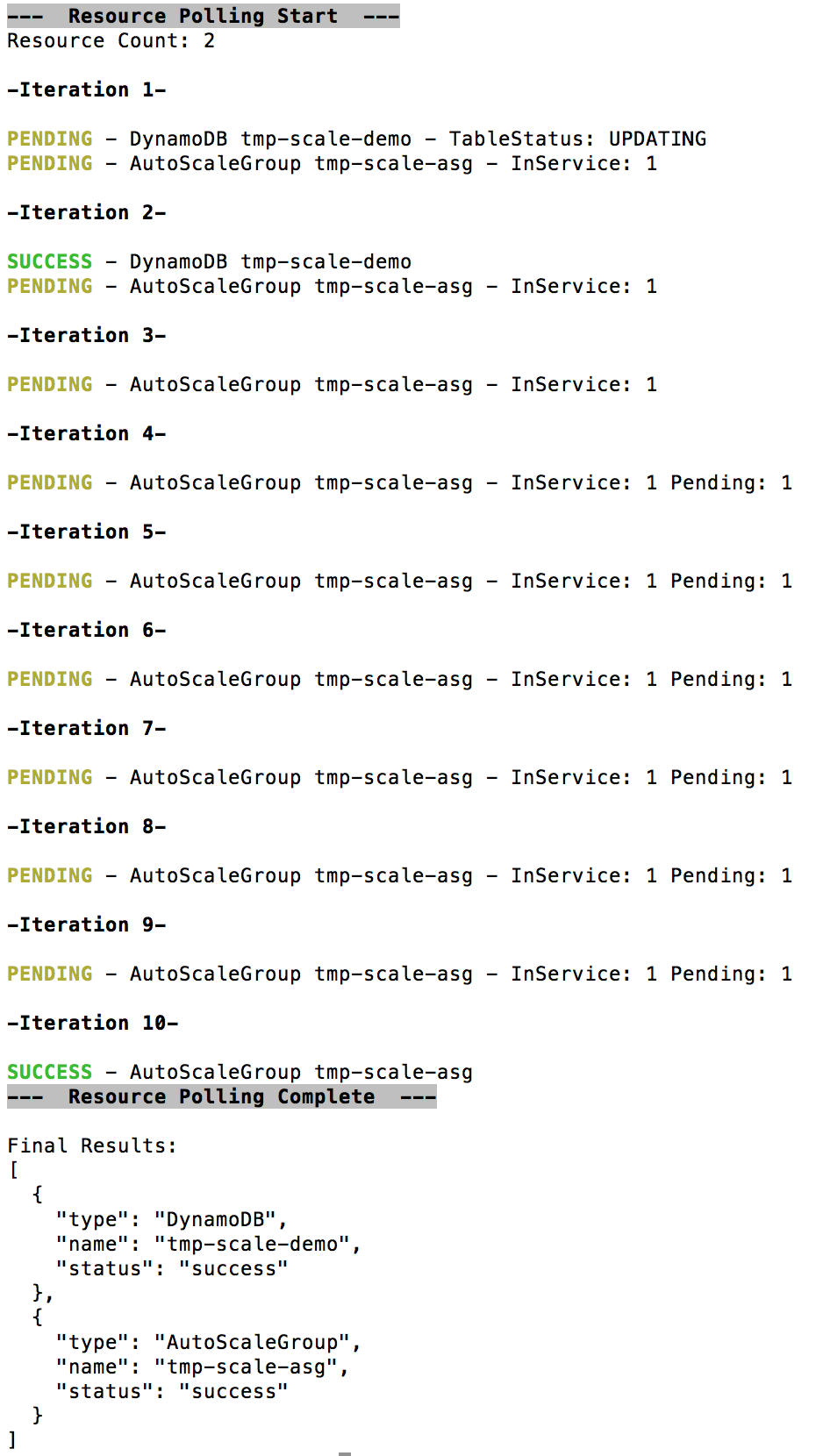
If you're scaling resources via node locally, aws-scale can poll your newly scaled resources and tell you when they're ready for use. If you're a developer waiting for a stack to come online this is much easier than digging through the console. To use polled, pass the following to your ResourceSet constructor:
var resourceSet = new scale.ResourceSet({pollScaleProgress: true});When using polling, the callback provided to resourceSet.scale(callback) will not be invoked until after
all resources have finished scaling to desired levels.
Resource Parameter Objects
The parameter objects passed to the resources are directly passed to an AWS Javascript SDK call. The contract for each of these resource parameter objects can be found at:
- scale.DynamoDB - AWS SDK DynamoDB.updateTable: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSJavaScriptSDK/latest/AWS/DynamoDB.html#updateTable-property
- scale.AutoScaleGroup - AWS SDK AutoScaling.setDesiredCapacity: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSJavaScriptSDK/latest/AWS/AutoScaling.html#setDesiredCapacity-property
Non-AWS Parameter Properties
The following resources have extra feature properties that can be set on the param object outside the scope of the AWS SDK:
-
scale.AutoScaleGroup
- params.setMinSize - if true, the auto scale group will have it's minimum number of instances set to params.DesiredCapacity before the desired capacity update is made. This is useful to make sure the ASG can always be scaled to the number of instances you want. Production CloudFormation scripts may want to enforce a minimum in production that can be ignored in test.
Example:
var asgParams = { AutoScalingGroupName: 'expressWebServiceASG', DesiredCapacity: 0, setMinSize: true // Defaults to false }; // After scaling this resource, the ASG will have minimum size and desired capacity set to zero. var asg = new scale.AutoScaleGroup(asgParams);
-
scale.DynamoDB
- params.ignoreUnchangedCapacityUpdates (Default: true) - AWS will throw an exception if table or global index throughput matches current read/write values. This can be an annoyance if running Aws-Scale nightly via lambda to reduce consumption. If tables are already scaled down, ignoreUnchangedCapacityUpdates set to true will ignore any index or table updates that already match desired levels. If set to false, all updates will be sent to AWS even if they match what's currently set for the table.
AWS Authorization
When running this library in lambda, you can use roles to grant the required permissions for the resources you are scaling. This link has details about modifying role permissions: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_manage_modify.html. Below is a list of actions each resource needs to scale properly:
- scale.DynamoDB:
- Action "dynamodb:UpdateTable"
- scale.AutoScaleGroup
- Action "autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup"
- Action "autoscaling:SetDesiredCapacity"
When running this library locally from Node, the following explains how to set credentials: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-javascript/v2/developer-guide/setting-credentials-node.html. I recommend using the ~/.aws/credentials file: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-javascript/v2/developer-guide/loading-node-credentials-shared.html.
Feature Features
This module is under active development and I'd like to add any helpful features you can think of. Please visit the github page to make any feature requests! Below are some of my next targets:
- Add Kinesis stream scaling.