Collection of code I use frequently in many of my projects. Especially the logging feature.
- Logging to console (colored) and file, in can be extended via additional writer via a plugin feature. The logging is done directly, but also can be done via a thread and a simple buffer.
You can install unqlite using pip.
pip install bbutils
Below is a sample designed to show some of the basic features and functionality of the logging library.
To begin, instantiate an Logging object. Then do the setup via log.setup(**kwargs).
log = Logging()
log.setup(app="example", level=3)- app: Application name
- use_thread: use threaded output
- interval: update interval for threaded mode in seconds
- level: verbose level (integer)
- index: dictionay with a lookup table for the different commands for each verbose level
index = {
0: ["INFORM", "WARN", "ERROR", "EXCEPTION", "TIMER", "PROGRESS"],
1: ["INFORM", "DEBUG1", "WARN", "ERROR", "EXCEPTION", "TIMER", "PROGRESS"],
2: ["INFORM", "DEBUG1", "DEBUG1", "WARN", "ERROR", "EXCEPTION", "TIMER", "PROGRESS"],
3: ["INFORM", "DEBUG1", "DEBUG2", "DEBUG3", "WARN", "ERROR", "EXCEPTION", "TIMER", "PROGRESS"]
}- console
- file
# We want console and file logging
console = log.get_writer("console")
fileio = log.get_writer("file")
# file name to log to
filename = os.path.abspath(os.path.normpath("{0:s}/run-tests.log".format(os.getcwd())))
# setup file and console output, set filename and filler for space for readable output.
console.setup(text_space=15)
fileio.setup(text_space=15, filename=filename)- text_space: number of space fillers for application name and tag
- seperator: seperator for tags and content, currently '|' as default
- error_index: list of commands (see Verbose level and the commands) redirected to stderr
- bar_len: length of progress bar
There are two modes for the file output. First is setting the filename directly. The second is setting filename, logname and logpath. The second enables to append a date and time value to the output filename.
- text_space: number of space fillers for application name and tag
- append_data: continue old logfile (only for filename)
- filename: filename for logfile (excludes logname, logpath and append_datetime)
- logname: general name for logfile (example logname=example will result in a filename of /exaple_2020-01-01_00.00.00.log)
- logpath: path to store the logfile, works only with logname
- append_datetime: add datetime to logname and logpath
Its possible to create self written writer and use these. Look in bbutil.logging.types for the Writer class and the Message class.
# register the output
log.register(console)
log.register(fileio)- inform(tag: str, content: str)
- warn(tag: str, content: str)
- debug1(tag: str, content: str)
- debug2(tag: str, content: str)
- debug3(tag: str, content: str)
- error(content: str)
- exception(e: Exception)
- traceback()
- progress(limit: int, interval: int = 0)
- timer(content: str)
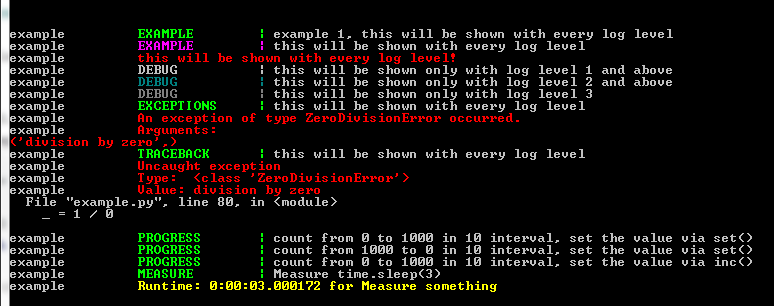
log.inform("EXAMPLE", "example 1, this will be shown with every log level")
example EXAMPLE | example 1, this will be shown with every log level
See file here
import os
import time
from bbutil.logging import Logging
if __name__ == '__main__':
log = Logging()
# Setup the logging, appicatio name is 'example', log level is 2
log.setup(app="example", level=3)
# We want console and file logging
console = log.get_writer("console")
fileio = log.get_writer("file")
# file name to log to
filename = os.path.abspath(os.path.normpath("{0:s}/run-tests.log".format(os.getcwd())))
# setup file and console output, set filename and filler for space for readable output.
console.setup(text_space=15)
fileio.setup(text_space=15, filename=filename)
# register the output
log.register(console)
log.register(fileio)
# switch logging on
log.open()
# example 1, this will be shown with every log level
log.inform("EXAMPLE", "example 1, this will be shown with every log level")
# example 2, this will be shown with every log level
log.warn("EXAMPLE", "this will be shown with every log level")
# error example, this will be shown with every log level
log.error("this will be shown with every log level!")
# debug 1 example, this will be shown only with log level 1 and above
log.debug1("DEBUG", "this will be shown only with log level 1 and above")
# debug 2 example, this will be shown only with log level 2 and above
log.debug2("DEBUG", "this will be shown only with log level 2 and above")
# debug 3 example, this will be shown only with log level 3
log.debug3("DEBUG", "this will be shown only with log level 3")
# show exceptions, this will be shown with every log level
log.inform("EXCEPTIONS", "this will be shown with every log level")
try:
_ = 1 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
log.exception(e)
# show traceback, this will be shown with every log level
log.inform("TRACEBACK", "this will be shown with every log level")
try:
_ = 1 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError:
log.traceback()
# show a progress meter via console
# first parameter: limit of the counter
# second parameter: update interval
# the update interval is there to prevent flickering, it also reduces the load
log.inform("PROGRESS", "count from 0 to 1000 in 10 interval, set the value via set()")
count1 = 0
progress1 = log.progress(1000, 10)
while True:
progress1.set(count1)
time.sleep(0.0001)
count1 += 1
if count1 > 1000:
break
# to remove the progress bar use clear
log.clear()
# it also can be used backwards
log.inform("PROGRESS", "count from 1000 to 0 in 10 interval, set the value via set()")
count2 = 1000
progress2 = log.progress(1000, 10)
progress2._counter = 1000
while True:
progress2.set(count2)
time.sleep(0.0001)
count2 -= 1
if count2 == 0:
break
# to remove the progress bar use clear
log.clear()
# now we use inc instead of setting the value
log.inform("PROGRESS", "count from 0 to 1000 in 10 interval, set the value via inc()")
count3 = 0
progress3 = log.progress(1000, 10)
while True:
progress3.inc()
time.sleep(0.0001)
count3 += 1
if count3 > 1000:
break
# to remove the progress bar use clear
log.clear()
log.inform("MEASURE", "Measure time.sleep(3)")
timer1 = log.timer("Measure something")
time.sleep(3)
timer1.stop()