Django Bootstrap 3 Boilerplate
Django Bootstrap 3 template project with class view feature
Current stable version: 0.0.8
Introduction
This project makes you to create a simple django project with Bootstrap 3 with minimal effort and with some common utils for you project.
Features
- Class oriented views.
- Simple Project creation with a single command line.
- Base classes for views, models and services with common methods for simpler usage of project classes.
Instalation
Installing Django Bootstrap is pretty straight forward, but some requirements must be made to be able to use this project:
Python 2.7
note
For future versions, the project will be Python 3.3+ compatible.
Some more requirements are also needed but are resolved on installed via pip, with the following command:
pip install django-classview-bootstrap3If you're installing with the targ.gz or zip distribution, you'll need to have these requirements installed in your python enviroment:
- django >= 1.6
- django_conventions
- django-webtest
- south
- dj_database_url
- simplejson
you can get them with the following command, after you have the project uncompressed:
pip install -r requirements.txtCreating a project
Creating a project is pretty simple, just issue the following command on your shell:
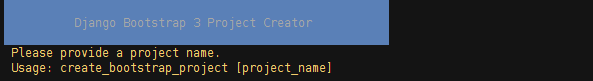
$ create_bootstrap_project <your_project_name>This command will create a project with the name passed as parameter. If no name has been issued with the command, expect the following output with this error:
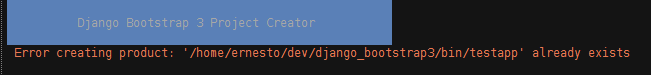
If the name of the project exists as a directory where you're issuing the command, expect the following output:
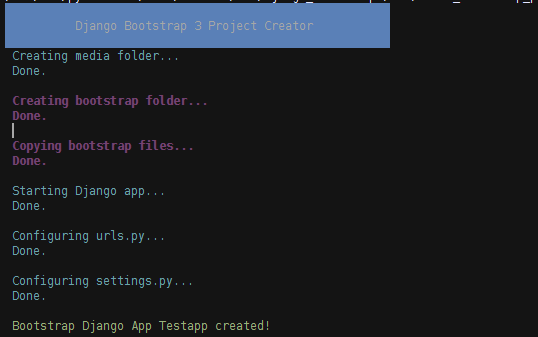
Otherwise the project will be created as follows (using testapp as the project name):
Base Model and extension
The boilerplate project comes with a Base Model class, with the following structure:
class BaseEntity(models.Model):
created_at = models.DateTimeField(null=True, blank=True)
updated_at = models.DateTimeField(null=True, blank=True)This class comes with two methods, fields and update_fields. The first one will get all the attributes excepting the private attributes (the ones starting with _). The latter method will get the same attributes excepting the fields included in NOT_IN_FIELDS, this constant is a list (by default this list is empty).
To be able to extend you models with these base class, just extend this base class as showed in the next example:
from django_bootstrap3view_app.models import BaseEntity
from django.db import models
class Person(BaseEntity):
SEX_CHOICES = (
('Male','M'),
('Female','F'),
)
age = models.IntegerField(null=True)
name = models.CharField(max_length=250, null=True, blank=True)
sex = models.CharField(max_length=2, choices=View classes and extensions
Service base class and extension
Service classes can be seen as classes that are between the model and the view and act like interfaces for a model class. For this, we have a base class for the services that will form part of the models.
The base class has methods such as all (that will get all the objects for the entity), get_one (that will get the first object based on the filter attributes passed as args or kwargs), _get_or_new (that based on a dictionary passed as parameter it'll get the object with those attributes or create an entity if no object has been found)
For more references for the base Service class see the section Reference of Service Class
Extending Service Class
To create a service class based on the base one, just follow the next example:
from my_bootstrap_app.models import Person
from django_bootstrap3view_app.services.base import BaseService
class PersonService(BaseService):
entity = Person
#define methods for you service.
Reference for Service Class
TBA
Thanks
Special thanks to jmg for helping me with the development of this project.