🗺 GeoMultipleChoice
A Django widget to select multiple geographic areas.
Originally created by @jeancochrane. Packaged up by @beamalsky.
Quick Start
This package is available for installation via PyPI. Simply run:
pip install django-geomultiplechoiceAdd it to INSTALL_APPS in your projects settings.py file:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'django_geomultiplechoice',
...
]You should now be ready to start widget setup following the documentation below.
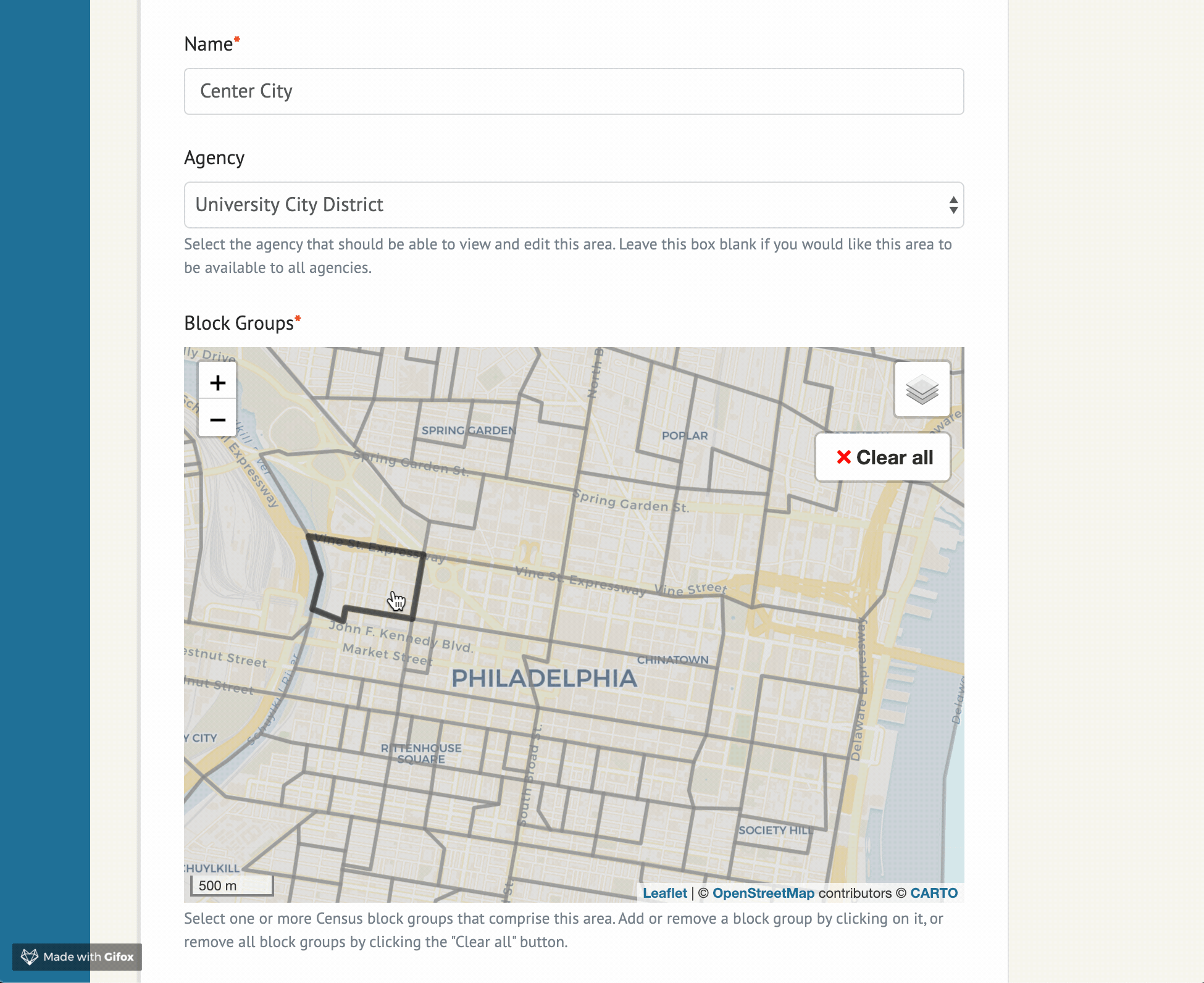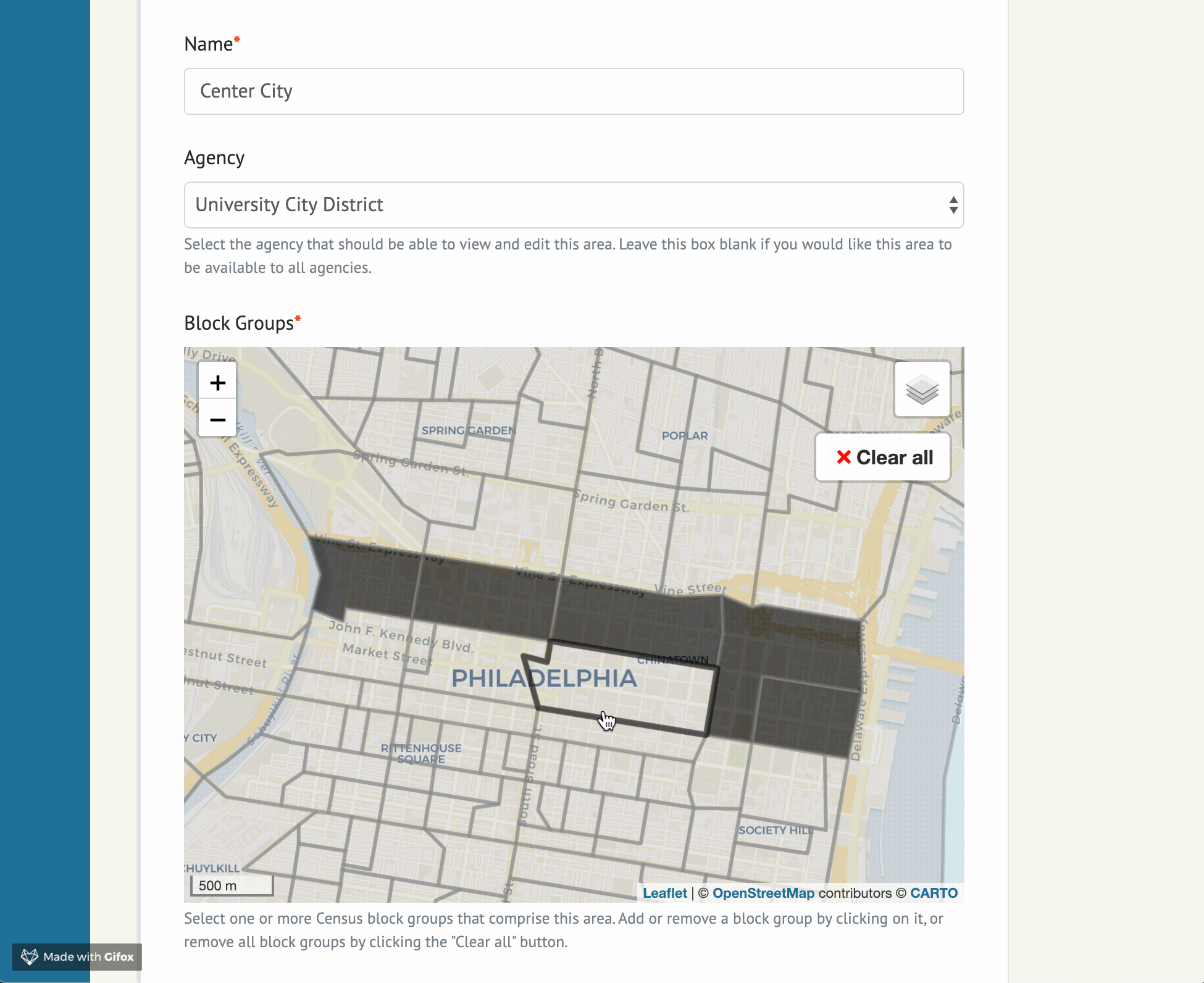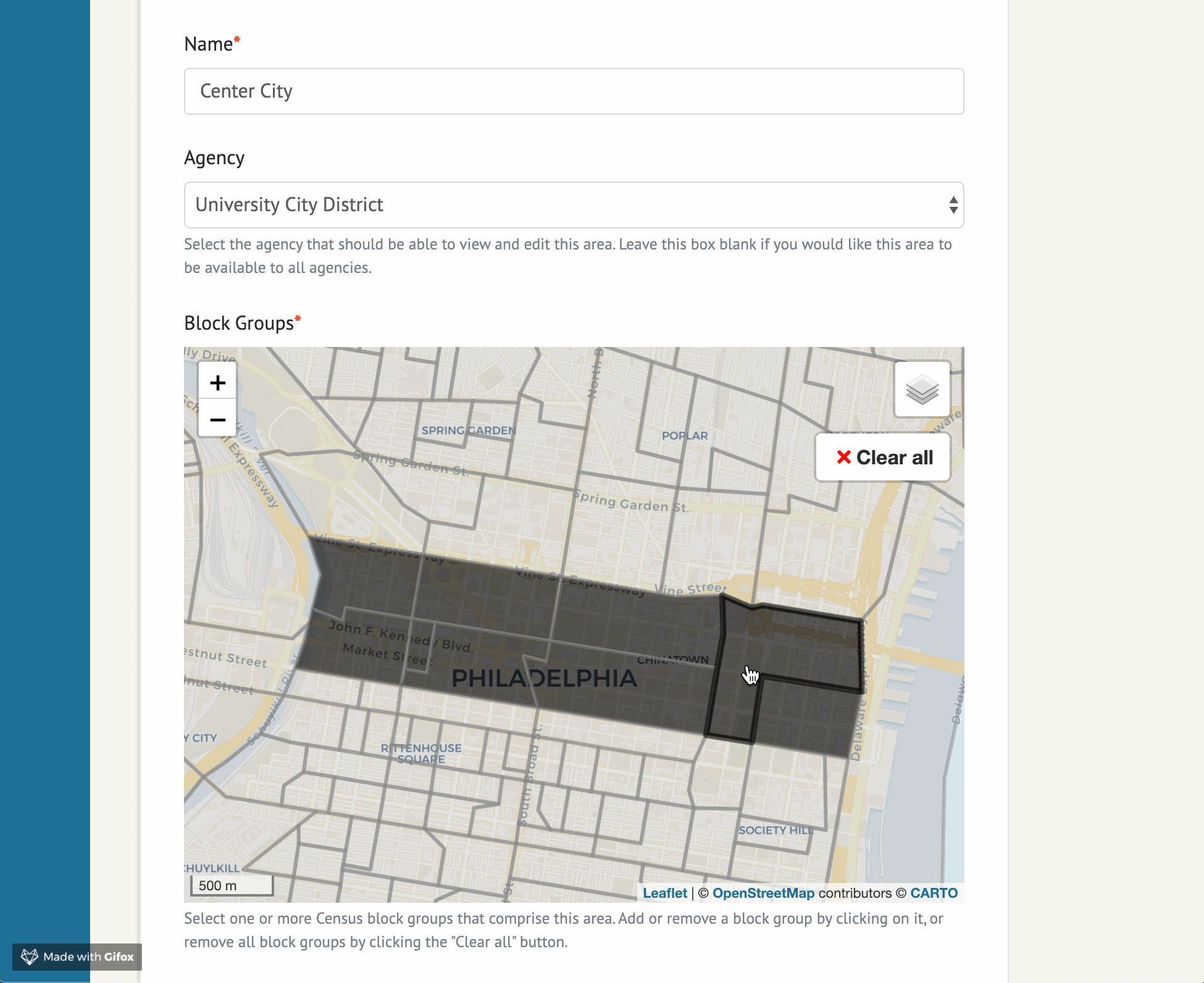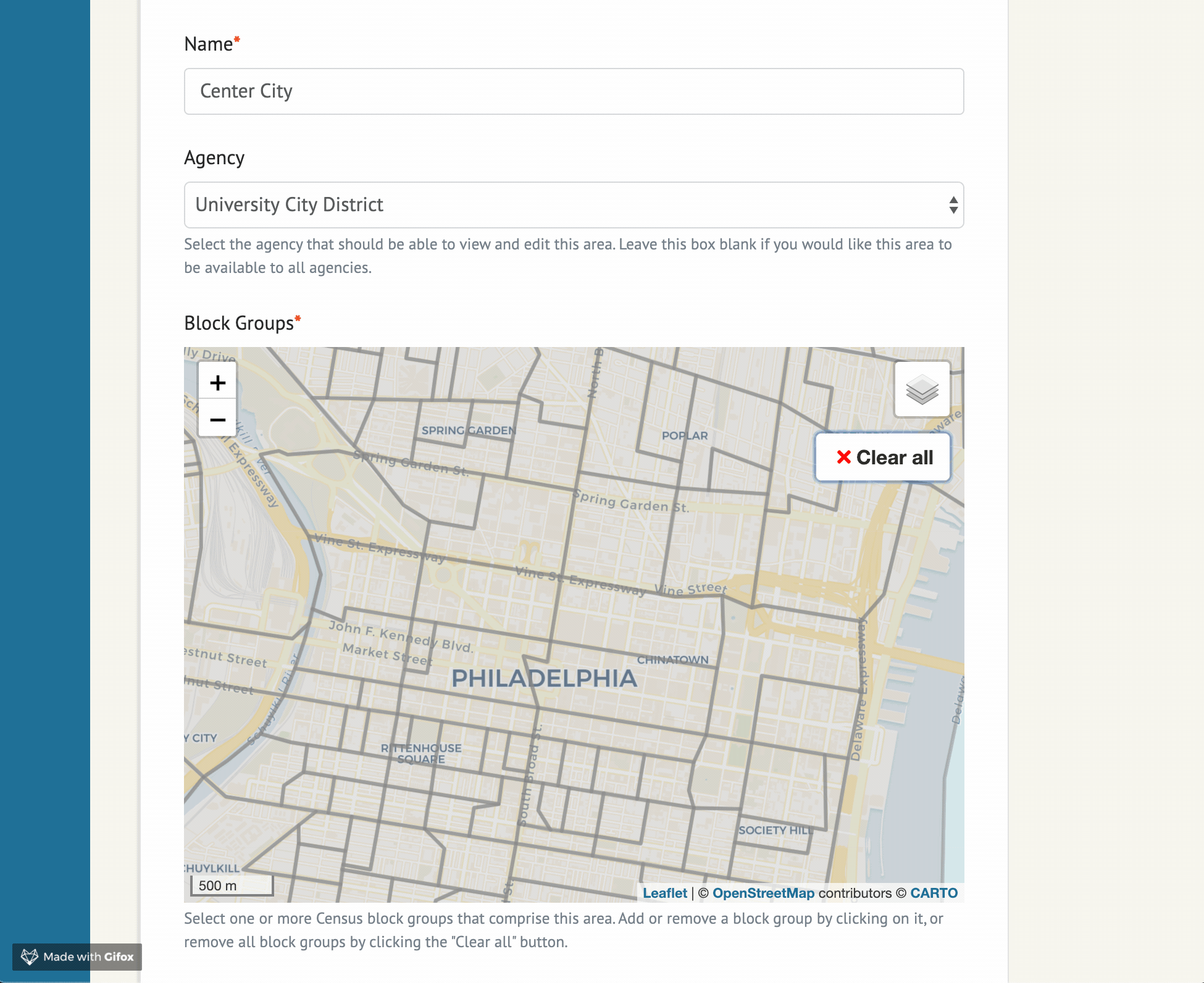
Widget options
The example project in this repo contains the following sample form implementation:
class ExampleGeoMultipleChoiceForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = SelectedArea
fields = '__all__'
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
settings_overrides = {
'DEFAULT_ZOOM': 12,
'DEFAULT_CENTER': (41.88, -87.7),
'RESET_VIEW' : True, # Defaults to True
# Sets the bounds of RESET VIEW; y min, x min, y max, x max
# See https://github.com/makinacorpus/django-leaflet/issues/192
'SPATIAL_EXTENT': (-87.3, 41.5, -88, 42.15),
'MAP_ID': 'my-example-map', # Defaults to 'map'
'MAP_HEIGHT': '400px',
'MAP_WIDTH': '100%',
'MAP_LAYER_STYLE': {
'color': '#7a7a7a',
'weight': 3,
'opacity': 0.5,
'fillColor': '#999999',
'fillOpacity': 0.3,
},
'MAP_LAYER_SELECTED_STYLE': {
'color': '#7a7a7a',
'weight': 3,
'opacity': 0.5,
'fillColor': 'black',
'fillOpacity': 0.7
}
}
self.fields['areas'].widget = GeoMultipleChoiceWidget(
choices=[
(choice.id, choice) for choice
in Area.objects.all()
],
settings_overrides=settings_overrides
)settings_overrides accepts all arguments used by django-leaflet in its LEAFLET_CONFIG, in addition to the following:
-
DEFAULT_ZOOMandDEFAULT_CENTERare required. -
MAP_IDsets the htmlidfor your widget map. Useful if you have multiple maps on the page. -
MAP_HEIGHTandMAP_WIDTHallow you to size the widget in your form. Must be used together. - This example uses the default values for
MAP_LAYER_STYLEandMAP_LAYER_STYLING.
SelectedArea is a model defined in example/models.py, and can be adjusted for your needs.
Importing Census data
This repo includes an example application using geographical data for 2018 Census block groups in Chicago. Look at data/Makefile and management/commands/import_data.py to see the ETL pipeline for that data.
If you'd like to use the same pipeline in your project but for a different area:
- Copy the
datadirectory into your project - Update
STATESinscripts/states.py. If the area is in a new state, create a new entry in STATES for that state; otherwise, update the existing state. - Update
allindata/Makefileto match the form$(DATA_DIR)/final/cb_2018_{state id}_bg_500k.shpfor each state you're importing shapefiles for. - To delete and regenerate the shapefiles, run:
cd data && make clean && makeOr if your app is containerized:
docker-compose run --rm app make clean -f example/data/Makefile
docker-compose run --rm app make -f example/data/Makefile- Run
python manage.py import_datato import the new geographical data. Or if your app is containerized, rundocker-compose run --rm app python manage.py import_data
Changing the data structure
Though the example implementation of this widget uses Census block groups, we've intentionally left the door open to varied geographic data. By default the widget expects each area to have the attributes in example.models.Area:
class Area(models.Model):
id = models.CharField(max_length=12, primary_key=True)
geom = geo_models.MultiPolygonField(srid=4269)If that structure doesn't work for you, it can be changed through creating a new widget that inherits from django_geomultiplechoice.widgets.GeoMultipleChoiceWidget and modifying get_features().
Local development
This app requires Docker and Docker Compose for local development.
To install and get started, run the following commands in your shell:
# Clone the repo
git clone git@github.com:datamade/django-geomultiplechoice.git
# Move into the folder
cd django-geomultiplechoice
Then build and run the app with Docker:
docker-compose up --buildYou'll also need to import the Census data into your database, for which we've provided a sample import_data.py. Open a new window in your terminal and run:
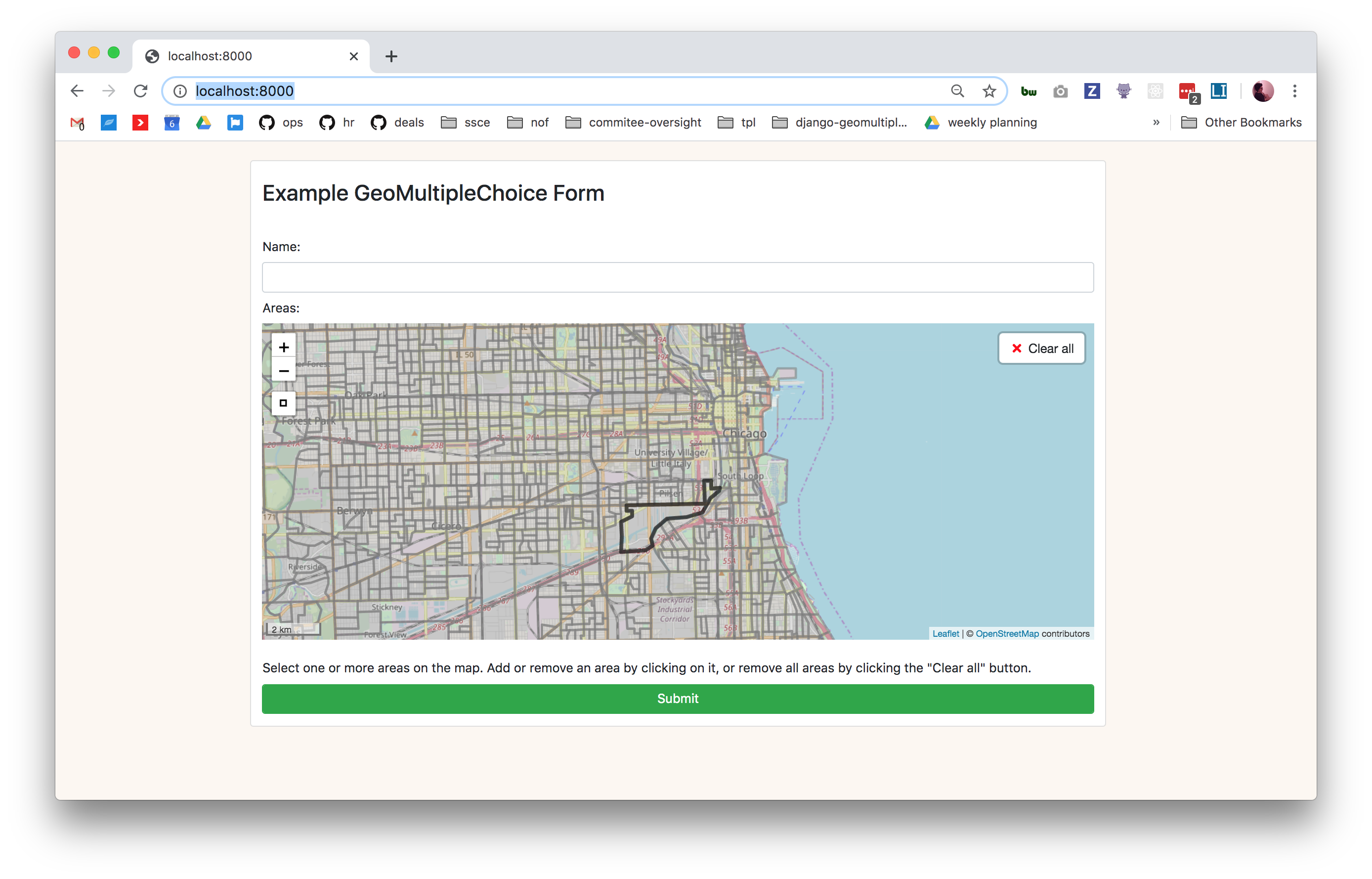
docker-compose run --rm app python manage.py import_dataVisit http://localhost:8000/ and you should see the example form running!
Cleaning up
To remove data files, run:
docker-compose run --rm app make clean -f example/data/MakefileTo regenerate the Census shapefiles, run:
docker-compose run --rm app make -f example/data/MakefileTo tear down the app and its volumes, run:
docker-compose down --volumes