About
This repository consists of a Python Module, which contains the core libraries for the HotWing-CLI and HotWing-GUI projects. This Module provides a series of classes and functions to aid in creating GCode for 4-Axis CNC foam cutters, specifically working with wing profiles, interpolating new profiles, and computing reverse kinematics for the CNC.
Installation
- Download or clone the Github repository.
- Open you Terminal or Command Line and navigate to the code (you should be in the file that contains the setup.py document).
cd /my/folder/hotwing-core - Install the module
pip install .
Docs
You can find the docs here : https://jasonhamilton.github.io/hotwing-core/index.html
Working With HotWing
Coordinate
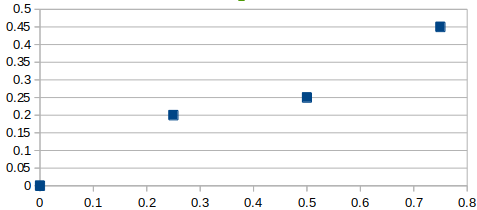
A Coordinate is the most basic building block. It represents a point in 2D space and simply contains x and y values. If we want to lay out some coordinates that look like:
We can use the following code:
from hotwing_core import Coordinate
c1 = Coordinate(0,0)
c2 = Coordinate(0.25,0.2)
c3 = Coordinate(0.5,0.25)
# you can add, subtract and multiply Coordinates
c4 = c2+c3 # 0.75,0.45You can find more info on the Coordinate's methods and functionality in the Documentation: https://jasonhamilton.github.io/hotwing-core/coordinate.html
Surface
A Surface is simply a list of Coordinates, which, when connected with lines, represents a Surface. A Surface contains the information to represent the top or bottom of an airfoil.
If we want to make something like this:
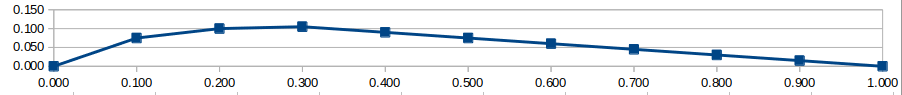
We can do so like:
from hotwing_core import Coordinate
from hotwing_core import Surface
# A list of coordinates that will make up a Surface
# These coordinates should be in either ascending or descending order based on the x value.
coords=[
Coordinate(1.000, 0.000),
Coordinate(0.900, 0.015),
Coordinate(0.800, 0.030),
Coordinate(0.700, 0.045),
Coordinate(0.600, 0.060),
Coordinate(0.500, 0.075),
Coordinate(0.400, 0.090),
Coordinate(0.300, 0.105),
Coordinate(0.200, 0.100),
Coordinate(0.100, 0.075),
Coordinate(0.000, 0.000)
]
s = Surface(coords)The Surface has a bunch of methods you can use, however you'll probably be interacting with the Profile method and letting it handle the lower-level interacton with the Surface object.
You can find more info on the Surface's methods and functionality in the Documentation https://jasonhamilton.github.io/hotwing-core/surface.html
Profile
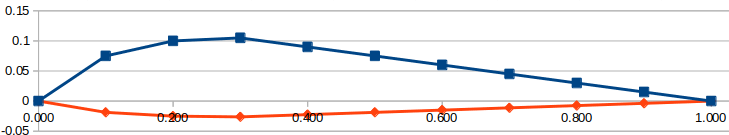
Next up is the Profile object. A profile is made up of two Surface objects a top and a bottom, which together make up a profile. A profile would look visually like:
You can create a profile using
from hotwing_core import Coordinate
from hotwing_core import Surface
from hotwing_core import Profile
top = [
Coordinate(1.000, 0.000),
Coordinate(0.900, 0.015),
Coordinate(0.800, 0.030),
Coordinate(0.700, 0.045),
Coordinate(0.600, 0.060),
Coordinate(0.500, 0.075),
Coordinate(0.400, 0.090),
Coordinate(0.300, 0.105),
Coordinate(0.200, 0.100),
Coordinate(0.100, 0.075),
Coordinate(0.000, 0.000),
]
bottom = [
Coordinate(1.000, 0),
Coordinate(0.900, -0.00375),
Coordinate(0.800, -0.0075),
Coordinate(0.700, -0.01125),
Coordinate(0.600, -0.015),
Coordinate(0.500, -0.01875),
Coordinate(0.400, -0.0225),
Coordinate(0.300, -0.02625),
Coordinate(0.200, -0.025),
Coordinate(0.100, -0.01875),
Coordinate(0.000, 0),
]
both = top+bottom
# You can create a profile from a list of Coordinates
p = Profile(both)
# You can create a Coordinate from two - top and bottom – Surface objects.
p = Profile(Surface(top),Surface(bottom))
# You can open an airfoil from dat (Selig or Lednicer format) a file on your hard drive
p = Profile("profiles/myprofile.dat")
# You can open an airfoil from dat (Selig or Lednicer format) via a URL:
p = Profile(“http://m-selig.ae.illinois.edu/ads/coord/e374.dat”)The Profile has lots of nifty methods built into it so you can rotate, trim, scale, offset, interpolate, etc. Check out the documentation here: https://jasonhamilton.github.io/hotwing-core/profile.html
Rib
A Rib is a representation of a slice of a wing. A Rib contains a Profile with the airfoil's coordinates, with which it can perform modifications such as scaling, offseting, rotating, and trimming for sheeting allowance (on the top or the bottom) and stock allowance (on the front or back).
from hotwing_core import Rib
## Create Rib
r1 = Rib("http://m-selig.ae.illinois.edu/ads/coord/e374.dat", # Dat file to use - File or URL
scale=10, # Width of the Rib - Scales the dat file profile
xy_offset=None, # Offset
top_sheet=0.0625, # Sheeting allowance top - this will make the foil smaller by this
# amount
bottom_sheet=0.0625, # Sheeting allowance bottom
front_stock=0.5, # Trims the front of the airfoil by this amount. You would glue
# wooden stock here and shape it
tail_stock=1.25, # Trims the trailing edge of the foil. You would put tail stock
# here and shape to the foil.
rotate=0, # The angle to rotate the rib in degrees - positive number points
# the nose upward
rotate_pos=0.5 ) # Where the rotation point should occur. 0.25 = 25% along the
# chord (starting from the front)
# you can get the manipulated profile
r1.sheeted_profile
# you can get the manipulated profile (pre-sheeting)
r1.profileDocumentation: https://jasonhamilton.github.io/hotwing-core/rib.html
Panel
A Panel contains two Ribs and makes up a panel of a wing. If you took the plywood ribs, placed them a distance apart, then sheeted them, you would get the equivalent of what a Panel represents.
from hotwing_core import Coordinate
from hotwing_core import Profile
from hotwing_core import Rib
from hotwing_core import Panel
## Create Root Rib
r1 = Rib("http://airfoiltools.com/airfoil/seligdatfile?airfoil=s6063-il",
scale=10,
xy_offset=None,
top_sheet=0.0625,
bottom_sheet=0.0625,
front_stock=0.5,
tail_stock=1.25 )
## Create Tip Rib
r2 = Rib("http://airfoiltools.com/airfoil/seligdatfile?airfoil=rg14-il",
scale=10,
xy_offset=Coordinate(0, 0),
top_sheet=0.0625,
bottom_sheet=0.0625,
front_stock=0.5,
tail_stock=1.25 )
# Setup Panel - takes the two ribs, at a specified distance of 24 units (inches or centimeters)
p = Panel(r1, r2, 24)
# A Panel can be trimmed. Say for example, the machine you will be using to cut your wing will
# only cut wings up to 12 units. We can use the Panel.trim_panel classmethod to create a new,
# Panel. The trim_panel will handle the interpolation and creation of a new Rib and Panel.
p1 = Panel.trim_panel(p, 0, 12)# cut at 0 (no cut will occur) and at 12 - new panel is 12 units long.
p2 = Panel.trim_panel(p, 12, 24)# cut at 12 and at 24 (no cut will occur) - new panel is 12 units long.Docs: https://jasonhamilton.github.io/hotwing-core/panel.html
Machine
A Machine is a representation of the 4-Axis CNC hotwire foam cutting machine. You pass the Machine a Panel object and the Machine will handle generating the Gcode for you.
from hotwing_core import Machine
# Setup Machine
m = Machine(24, # Width between pillars of machine
kerf=0.075, # Allowance for wire size and melted foam
profile_points=200, # number of points to use for each surface when
# iterpolating
output_profile_images=False) # generates image of the Profile and Rib manipulation for
# Debugging
# Load panel into machine (p1 is the panel created in the previous step)
# The offset is the distance the left of the panel will be from the left of the machine --
# If you want it centered, for this example use an offset of 6 --
# (24-12[machine width-panel width]) -> 12/2(equal amount on each side)
m.load_panel(panel=p1,left_offset=6)
# Generate GCode
# safe_height is where the machine can move without hitting anything
gcode = m.generate_gcode(safe_height=5)
# Output to screen
print gcodeDocs: https://jasonhamilton.github.io/hotwing-core/machine.html
Putting it All Together
from hotwing_core import Profile
from hotwing_core import Rib
from hotwing_core import Machine
from hotwing_core import Panel
from hotwing_core import Coordinate
## Setup Rib
r1 = Rib("http://airfoiltools.com/airfoil/seligdatfile?airfoil=s6063-il",
scale=10,
xy_offset=None,
top_sheet=0.0625,
bottom_sheet=0.0625,
front_stock=0.5,
tail_stock=1.25 )
r2 = Rib("http://airfoiltools.com/airfoil/seligdatfile?airfoil=rg14-il",
scale=10,
xy_offset=Coordinate(0, 0),
top_sheet=0.0625,
bottom_sheet=0.0625,
front_stock=0.5,
tail_stock=1.25 )
# Setup Panel
p = Panel(r1, r2, 24)
# Trim Panel
p1 = Panel.trim_panel(p, 0, 12)
# Setup Machine
m = Machine(24, kerf=0.075, profile_points=200, output_profile_images=False)
# Load panel into machine
m.load_panel(panel=p1,left_offset=6)
m.gcode_formatter_name = "debug"
# Generate GCode
gcode = m.generate_gcode(safe_height=5)
# Output to screen
print gcodeTesting
Tests are located in the test folder. Make sure you have the dependencies in requirements_dev.txt installed.
From the root folder (hotwing-core) run:
# Run all tests
pytest
# Run tests but allow print statements to output text - useful for debugging
pytest -s
# Run tests and show coverage
pytest --cov=hotwing_core
# Run tests, show coverage and show lines not covered by tests
pytest --cov=hotwing_core --cov-report term-missing