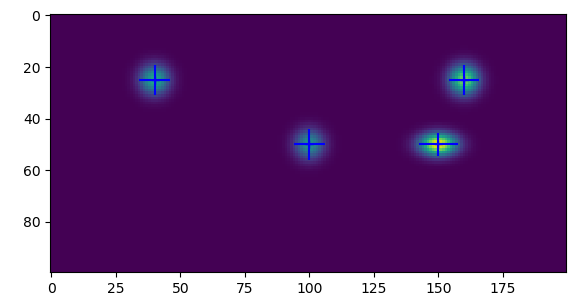
BLOBs
Analysis of gray scale images containing gaussian shaped blobs.
Blobs should not overlap in 2d, but may overlap in projection.
Entry point is blobs.find_blobs().
from image_blobs import find_blobs
from image_blobs.util import make_image, show_features
shape = (100, 200) # 200x100
Fs = [
# X Y W H A IDX (ignored as input, unique in output)
(160, 25, 4, 4, 4, 0),
(150, 50, 5, 3, 5, 0),
( 40, 25, 4, 4, 3, 0),
(100, 50, 4, 4, 2.5, 0),
]
print('Actual')
print(Fs)
img = make_image(shape, Fs, dtype='u1')
features = find_blobs(img)
print('Computed (order may differ)')
print(features)
show_features(img, features, sigma=3)Details
Result X/Y and W/H are given as coordinates as an image is typically rendered.
eg. A 200x100 image has 200 pixels in X.
Scipy stores images with the order of dimensions reversed.
eg. 200x100 becomes shape=(100, 200).
The find_blobs() function works by first identifying
contiguous blobs of pixels with scipy.ndimage.label().
This step works best when each blob is well isolated
from the background.
Then, a bounded fit to a 2d gaussian is made individually
for each blob using scipy.optimize.least_squares().
This fit is performed against the sub-image bounding each feature.
So small features can be fit relatively quickly.