Pyramid Mongodb
A simple library to integrate mongodb into your pyramid application. Comes with a debugtoolbar.
Features
- Supports multiple databases
- Configuration only setup
- Integrated debugtoolbar with:
- Shows db response times
-
explain()for cursor results - Connection information
- Database and collection stats
- Avoids recreating and closing
MongoClienton every request.
Setup
pip install pyramid_mongodb2Add the following to your application's ini file, (include pyramid_mongodb2:MongoToolbar in debugtoolbar.includes if you want to debug):
[app:main]
mongo_uri = mongodb://username:password@mongodb.host.com:27017/authdb
mongo_dbs =
foo
bar
baz-quux
foo-test = foo
pyramid.includes =
pyramid_mako
pyramid_debugtoolbar
pyramid_mongodb2
debugtoolbar.includes =
pyramid_mongodb2:MongoToolbarThe code will use config.add_request_method() to add a Database object to your requests, where each database is accessible by db_database_name, as defined in your configuration.
Note: database names with hyphens in them will be converted to underscores, that is database baz-quux will be accessible by request.db_baz_quux.
When doing foo-test = foo, the mongodb database with name foo-test will be assigned to request.db_foo.
This helps when testing so that you can use a separate database for development, testing and production without
changing your application code, or if you just want to alias a database name.
In your code where you can access request, you now have the following variables:
request.db
request.db_foo
request.db_bar
request.db_baz_quux
request.db_foorequest.db is the MongoClient object, should you ever need it.
In your view code, you can do this:
from pyramid.view import view_config
@view_config(route_name='home', renderer="templates/landing.mako")
def my_view(request):
return {
'some_data': request.db_foo.some_collection.find({'a': {'$gte': 5}}, {'_id': False}),
'other_data': request.db_bar.visitors.insert_one({'person': request.remote_addr}),
}Debugging
With debugging enabled, all queries will be logged in request.query_log, when the debugtoolbar is opened, you can
then view the execution time and explain() of cursor results. You can also see connection settings and stats for
databases and collections.
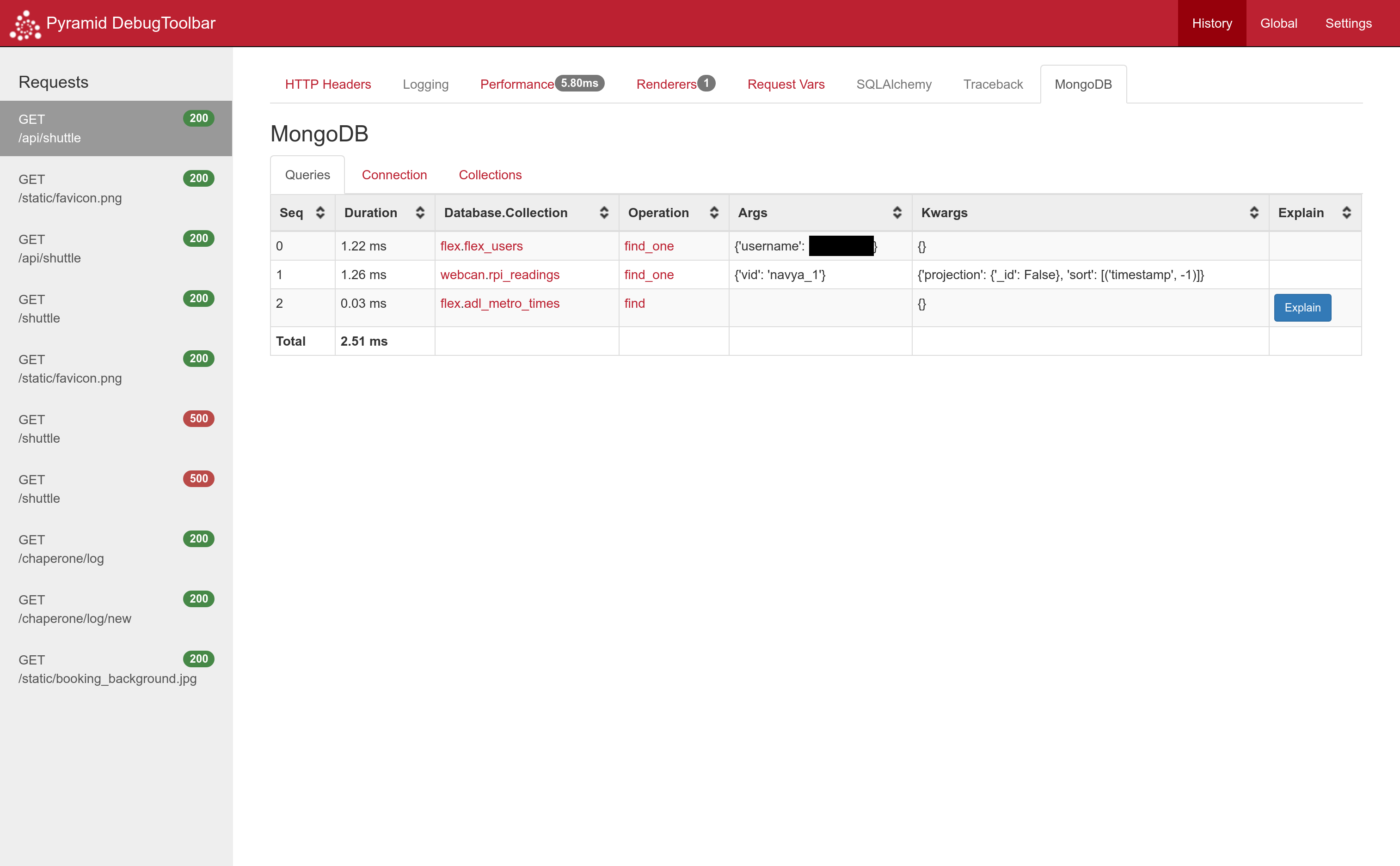
Screenshots
Here's what the toolbar looks like in action:
Clicking the database or collection name will take you to the relevant section of the collections tab. Clicking the operation name will take you to its pymongo documentation.

Clicking the explain button will show you the explain() result for a cursor.
 You can view detailed connection information here, clicking the field name will take you to the pymongo documentation for that field.
You can view detailed connection information here, clicking the field name will take you to the pymongo documentation for that field.
 This page show
This page show dbstats for all connected databases used in this request and their collections.
 Here we can see the use of multiple databases in a single project.
Here we can see the use of multiple databases in a single project.