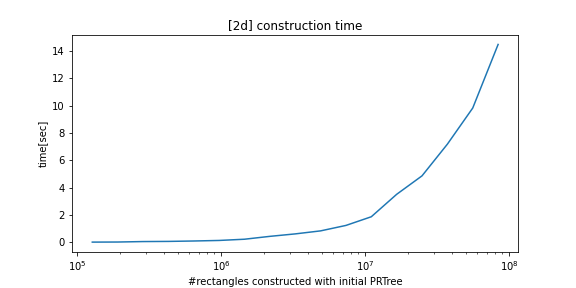
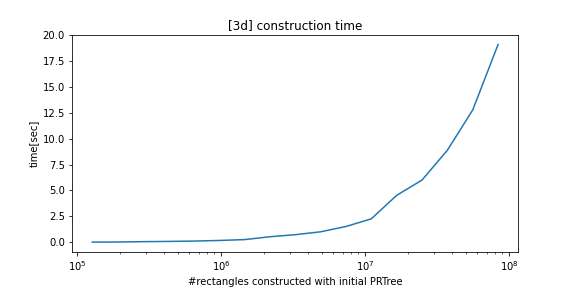
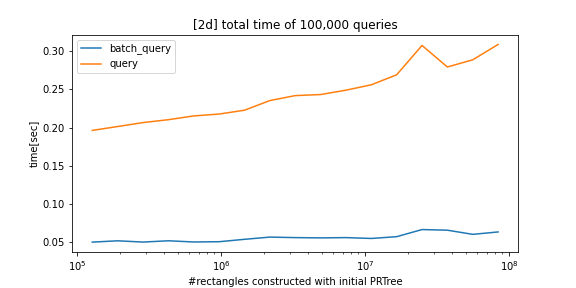
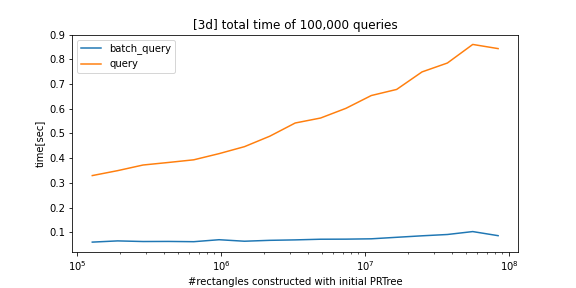
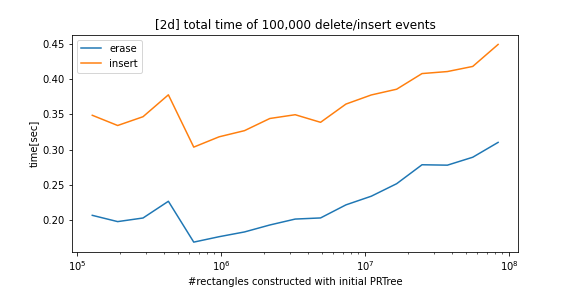
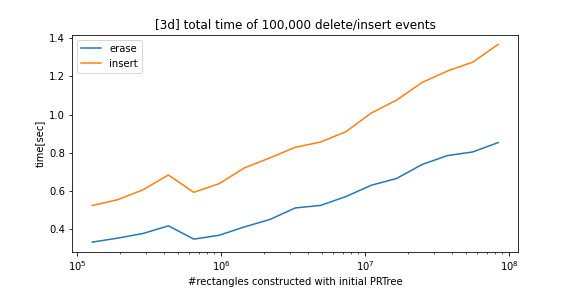
python_prtree is a python/c++ implementation of the Priority R-Tree (see references below), an alternative to R-Tree. The supported futures are as follows:
- Construct a Priority R-Tree (PRTree) from an array of rectangles.
-
PRTree2D,PRTree3DandPRTree4D(2D, 3D and 4D respectively)
-
-
insertanderase- The
insertmethod can be passed pickable Python objects instead of int64 indexes.
- The
-
queryandbatch_query-
batch_queryis parallelized bystd::threadand is much faster than thequerymethod. - The
querymethod has an optional keyword argumentreturn_obj; ifreturn_obj=True, a Python object is returned.
-
-
rebuild- It improves performance when many insert/delete operations are called since the last rebuild.
- Note that if the size changes more than 1.5 times, the insert/erase method also performs
rebuild.
This package is mainly for mostly static situations where insertion and deletion events rarely occur.
You can install python_prtree with the pip command:
pip install python-prtreeIf the pip installation does not work, please git clone clone and install as follows:
pip install -U cmake pybind11
git clone --recursive https://github.com/atksh/python_prtree
cd python_prtree
python setup.py installimport numpy as np
from python_prtree import PRTree2D
idxes = np.array([1, 2])
# rects is a list of (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
rects = np.array([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5],
[1.0, 1.5, 1.2, 3.0]])
prtree = PRTree2D(idxes, rects)
# batch query
q = np.array([[0.5, 0.2, 0.6, 0.3],
[0.8, 0.5, 1.5, 3.5]])
result = prtree.batch_query(q)
print(result)
# [[1], [1, 2]]
# You can insert an additional rectangle by insert method,
prtree.insert(3, np.array([1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0]))
q = np.array([[0.5, 0.2, 0.6, 0.3],
[0.8, 0.5, 1.5, 3.5]])
result = prtree.batch_query(q)
print(result)
# [[1], [1, 2, 3]]
# Plus, you can erase by an index.
prtree.erase(2)
result = prtree.batch_query(q)
print(result)
# [[1], [1, 3]]
# Non-batch query is also supported.
print(prtree.query([0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0]))
# [1, 3]
# Point query is also supported.
print(prtree.query([0.5, 0.5]))
# [1]
print(prtree.query(0.5, 0.5)) # 1d-array
# [1]import numpy as np
from python_prtree import PRTree2D
objs = [{"name": "foo"}, (1, 2, 3)] # must NOT be unique but pickable
rects = np.array([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5],
[1.0, 1.5, 1.2, 3.0]])
prtree = PRTree2D()
for obj, rect in zip(objs, rects):
prtree.insert(bb=rect, obj=obj)
# returns indexes genereted by incremental rule.
result = prtree.query((0, 0, 1, 1))
print(result)
# [1]
# returns objects when you specify the keyword argment return_obj=True
result = prtree.query((0, 0, 1, 1), return_obj=True)
print(result)
# [{'name': 'foo'}]The 1d-array batch query will be implicitly treated as a batch with size = 1.
If you want 1d result, please use query method.
result = prtree.query(q[0])
print(result)
# [1]
result = prtree.batch_query(q[0])
print(result)
# [[1]]You can also erase(delete) by index and insert a new one.
prtree.erase(1) # delete the rectangle with idx=1 from the PRTree
prtree.insert(3, np.array([0.3, 0.1, 0.5, 0.2])) # add a new rectangle to the PRTreeYou can save and load a binary file as follows.
# save
prtree.save('tree.bin')
# load with binary file
prtree = PRTree('tree.bin')
# or defered load
prtree = PRTree()
prtree.load('tree.bin')Note that cross-version compatibility is NOT guaranteed, so please reconstruct your tree when you update this package.
- The insert method has been improved to select the node with the smallest mbb expansion.
- The erase method now also executes rebuild when the size changes by a factor of 1.5 or more.
- You can use PRTree4D.
- Add compression for pickled objects.
You can use pickable Python objects instead of int64 indexes for insert and query methods:
- Changed the input order from (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax, ...) to (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, ...).
- Added rebuild method to build the PRTree from scratch using the already given data.
- Fixed a bug that prevented insertion into an empty PRTree.
- You can use PRTree3D:
The Priority R-Tree: A Practically Efficient and Worst-Case Optimal R-Tree Lars Arge, Mark de Berg, Herman Haverkort, and Ke Yi Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD '04), Paris, France, June 2004, 347-358. Journal version in ACM Transactions on Algorithms. author's page