scikits.pulsefit
A pulse-fitting library for python.
Work in Progress
This is a work in progress. The interface will be stabilized after I get some feedback. Please feel free to get in touch if you have any questions, comments, or suggestions.
I'd also be interested in any out of the ordinary real-world pulse shapes to test with.
To-do List
- Automatic noise estimation for reduced chi^2 computation?
Overview
The pulsefit package provides functions allowing one to identify the
positions and amplitudes of a characteristic pulse shape within a
larger data array.
Features
- Robust fitting in the face of overlapping pulses.
- Linear interpolation for continuous pulse locations.
- Fast moving-median filter for establishing the baseline.
- Good performance from key components written in C.
The pulsefit package currently provides a single function,
fit_mpoc_mle. This function takes a fairly large number of
parameters that determine the fitting behavior.
Example usage
import numpy as np
#from scikits.pulsefit import fit_mpoc_mle
from scikits.pulsefit import fit_viewer
# Create a characteristic pulse shape.
width = 10.0
tau = width / 2
x = np.arange(0, 10*width, dtype=np.float64)
p = (1*x/tau) * np.exp(-x/tau)
p /= p.max()
# Generate some noise.
sigma = 0.25
d = np.random.normal(2.0, sigma, 100000)
# Generate a uniform distribution of pulses.
n_pulses = int(len(d) / 100)
inds0 = np.random.uniform(0, len(d) - 1, n_pulses)
inds0.sort()
amps0 = np.random.uniform(2.0, 5.0, n_pulses)
for (idx, amp) in zip(inds0, amps0):
f_idx = np.floor(idx)
xp = np.arange(len(p))
x = xp - (idx % 1)
di = min(len(p), len(d) - idx - 1)
d[f_idx:f_idx + di] += amp * np.interp(x, xp, p)[:di]
# View fits.
fit_viewer.view(
d, p,
th=1.5,
th_min=1.0,
filt_len=100,
pad_pre=20,
pad_post=50,
max_len=768,
min_denom=0.15,
exclude_pre=10,
exclude_post=50,
p_err_len=40,
sigma2=sigma*sigma,
chi2red_max=2.0,
correct=True,
pulse_add_len=70,
pulse_min_dist=2)The view function is provided as a way to conveniently review blocks
as they're fit. It has the same signature as the fit_mpoc_mle
function.
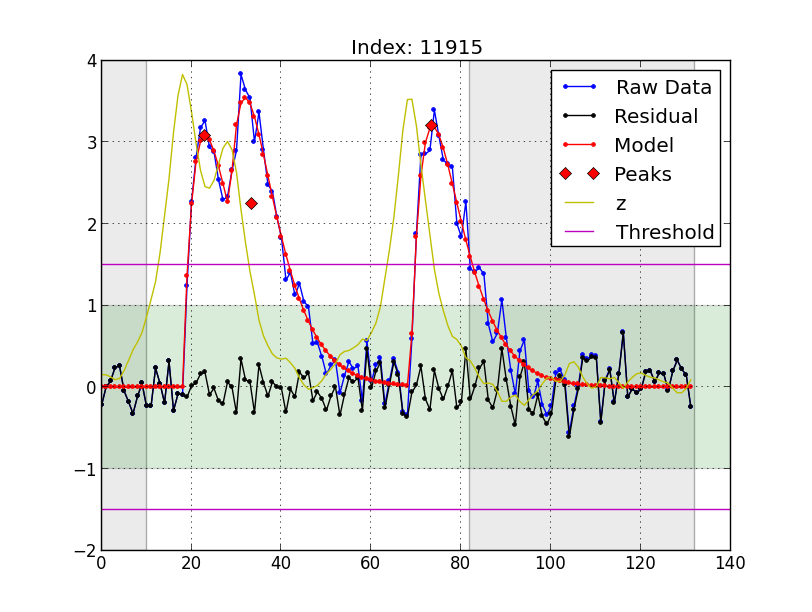
Here's an example plot of one block:
Each plot shows a single block. The following information is plotted:
-
Raw Datais the data we'd like to fit with some number of pulses. -
Residualis the residual after the bset-fit pulses have been subtracted fromRaw Data. -
Modelis the best fit to the data that was obtained. -
Peaksmark the peak of each fit pulse. -
zis the output of the modified phase-only correlation (MPOC) algorithm used to initially identify the pulse positions. Themin_denomparameter acts as a low-pass filter onz. -
Thresholdis thethparameter. - The green shaded region indicates the lowest amplitude pulse that
will be fit, given by the parameter
th_min. - The grey shaded regions are the excluded regions. These are
controled by
exclude_preandexclude_post.