pl-z2labelmap

Table of Contents
Abstract
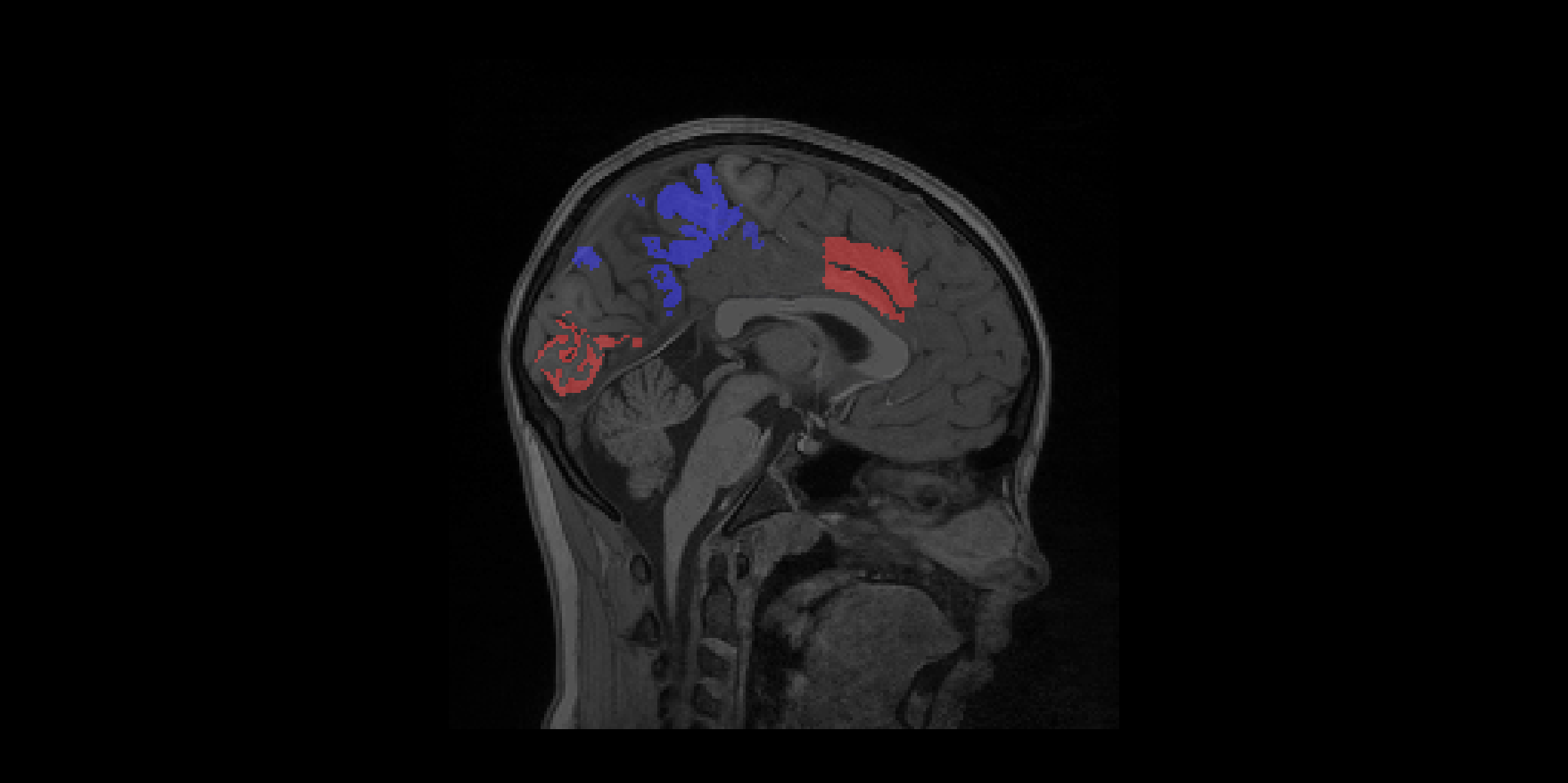
zlabelmap.py generates FreeSurfer labelmaps from z-score vector files. These labelmap files are used by FreeSurfer to color-code parcellated brain regions. By calculating a z-score to labelmap transform, we are able to show a heat map and hightlight brain regions that differ from some comparative reference, as demonstrasted below
where positive volume deviations of a parcellated brain region are shown in red (i.e. the subject had a larger volume in that area than the reference), and negative volume deviations are shown in blue (i.e. the subject had a smaller volume in that area than reference).
Note that these are randomly generated z-scores purely for illustrative purposes.
Essentially the script consumes an input text vector file of
<str_structureName> <float_lh_zScore> <float_rh_zScore>
for example,
G_and_S_frontomargin ,1.254318450576827,-0.8663546810093861
G_and_S_occipital_inf ,1.0823728865077271,-0.7703944006354377
G_and_S_paracentral ,0.20767669866335847,2.9023126278939912
G_and_S_subcentral ,2.395503357157743,-1.4966482475891556
G_and_S_transv_frontopol ,-1.7849555258577423,-2.461419463760234
G_and_S_cingul-Ant ,-2.3831737860960382,1.1892593438667625
G_and_S_cingul-Mid-Ant ,0.03381695289572084,-0.7909116233500506
G_and_S_cingul-Mid-Post ,-2.4096082230335485,1.166457973597625
...
...
S_postcentral ,1.3277159068067768,-1.4042773812503526
S_precentral-inf-part ,-1.9467169777576718,1.7216636236995733
S_precentral-sup-part ,0.764673539853991,2.1081570332369504
S_suborbital ,0.522368665639954,-2.3593237820349007
S_subparietal ,-0.14697262729901928,-2.2116605141889094
S_temporal_inf ,-1.8442944920810271,-0.6895142771486307
S_temporal_sup ,-1.8645248463693804,2.740099589311164
S_temporal_transverse ,-2.4244451521560073,2.286596403222344
and creates a FreeSurfer labelmap where <str_structureName> colors correspond to the z-score (normalized between 0 and 255).
Currently, only the aparc.a2009s FreeSurfer segmentation is fully supported, however future parcellation support is planned.
Negative z-scores and positive z-scores are treated in the same manner but have sign-specific color specifications. Positive and negative z-Scores can be assigned some combination of the chars RGB to indicate which color dimension will reflect the z-Score. For example, a
--posColor R --negColor RG
will assign positive z-scores shades of red and negative z-scores shades of yellow (Red + Green = Yellow).
Synopsis
python z2labelmap.py \
[-v <level>] [--verbosity <level>] \
[--random] [--seed <seed>] \
[-p <f_posRange>] [--posRange <f_posRange>] \
[-n <f_negRange>] [--negRange <f_negRange>] \
[-P <'RGB'>] [--posColor <'RGB'>] \
[-N <'RGB'>] [--negColor <'RGB'>] \
[--imageSet <imageSetDirectory>] \
[-s <f_scaleRange>] [--scaleRange <f_scaleRange>] \
[-l <f_lowerFilter>] [--lowerFilter <f_lowerFilter>] \
[-u <f_upperFilter>] [--upperFilter <f_upperFilter>] \
[-z <zFile>] [--zFile <zFile>] \
[--version] \
[--man] \
[--meta] \
<inputDir> \
<outputDir>
Run
This plugin can be run in two modes: natively as a python package or as a containerized docker image.
Using PyPI
To run from PyPI, simply do a
pip install z2labelmapand run with
z2labelmap.py --man /tmp /tmpto get inline help.
Using docker run
To run using docker, be sure to assign an "input" directory to /incoming and an output directory to /outgoing. Make sure that the $(pwd)/out directory is world writable!
Now, prefix all calls with
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/in:/incoming -v $(pwd)/out:/outgoing \
fnndsc/pl-z2labelmap z2labelmap.py \Thus, getting inline help is:
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/in:/incoming -v $(pwd)/out:/outgoing \
fnndsc/pl-z2labelmap z2labelmap.py \
--man \
/incoming /outgoingExamples
Create a sample/random z-score file and analyze
- In the absense of an actual z-score file, the script can create one. This can then be used in subsequent analysis:
mkdir in out
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/in:/incoming -v $(pwd)/out:/outgoing \
fnndsc/pl-z2labelmap z2labelmap.py \
--random --seed 1 \
--posRange 3.0 --negRange -3.0 \
/incoming /outgoing
or without docker
mkdir in out
z2labelmap.py \
--random --seed 1 \
--posRange 3.0 --negRange -3.0 \
/in /out
In this example, z-scores range between 0.0 and (+/-) 3.0.
Generate labelmap and also copy pre-calculated image set to output
- Analyze a file already located at
in/zfile.csvand copy pre-calculated image data
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/in:/incoming -v $(pwd)/out:/outgoing \
fnndsc/pl-z2labelmap z2labelmap.py \
--negColor B --posColor R \
--imageSet ../data/set1 \
/incoming /outgoing
This assumes a file called 'zfile.csv' in the <inputDirectory> that ranges in z-score between 0.0 and 3.0, and uses the --scaleRange to reduce the apparent brightness of the map by 50 percent. Furthermore, the lower 80 percent of z-scores are removed (this has the effect of only showing the brightest 20 percent of zscores).
Control relative brightness and lower filter low z-scores from final labelmap
- To analyze a file already located at
in/zfile.csv, apply ascaleRangeand also filter out the lower 80% of z-scores:
docker run --rm -v $(pwd)/in:/incoming -v $(pwd)/out:/outgoing \
fnndsc/pl-z2labelmap z2labelmap.py \
--scaleRange 2.0 --lowerFilter 0.8 \
--negColor B --posColor R \
/incoming /outgoing
This assumes a file called 'zfile.csv' in the <inputDirectory> that ranges in z-score between 0.0 and 3.0, and uses the --scaleRange to reduce the apparent brightness of the map by 50 percent. Furthermore, the lower 80 percent of z-scores are removed (this has the effect of only showing the brightest 20 percent of zscores).
Using the above referenced z-score file, this results in:
0 Unknown 0 0 0 0
11101 lh-G_and_S_frontomargin 0 0 0 0
11102 lh-G_and_S_occipital_inf 0 0 0 0
11103 lh-G_and_S_paracentral 0 0 0 0
11104 lh-G_and_S_subcentral 103 0 0 0
11105 lh-G_and_S_transv_frontopol 0 0 0 0
11106 lh-G_and_S_cingul-Ant 0 0 110 0
11107 lh-G_and_S_cingul-Mid-Ant 0 0 0 0
11108 lh-G_and_S_cingul-Mid-Post 0 0 111 0
...
...
12167 rh-S_postcentral 0 0 0 0
12168 rh-S_precentral-inf-part 0 0 0 0
12169 rh-S_precentral-sup-part 0 0 0 0
12170 rh-S_suborbital 0 0 110 0
12171 rh-S_subparietal 0 0 103 0
12172 rh-S_temporal_inf 0 0 0 0
12173 rh-S_temporal_sup 119 0 0 0
12174 rh-S_temporal_transverse 0 0 0 0
Command line arguments
<inputDir> Required argument. Input directory for plugin. <outputDir> Required argument. Output directory for plugin. [-v <level>] [--verbosity <level>] Verbosity level for app. Not used currently. [--random] [--seed <seed>] If specified, generate a z-score file based on <posRange> and <negRange>. In addition, if a further optional <seed> is passed, then initialize the random generator with that seed, otherwise system time is used. [-p <f_posRange>] [--posRange <f_posRange>] Positive range for random max deviation generation. [-n <f_negRange>] [--negRange <f_negRange>] Negative range for random max deviation generation. [-P <'RGB'>] [--posColor <'RGB'>] Some combination of 'R', 'G', B' for positive heat. [-N <'RGB'> [--negColor <'RGB'>] Some combination of 'R', 'G', B' for negative heat. [--imageSet <imageSetDirectory>] If specified, will copy the (container) prepopulated image set in <imageSetDirectory> to the output directory. [-s <f_scaleRange>] [--scaleRange <f_scaleRange>] Scale range for normalization. This has the effect of controlling the brightness of the map. For example, if this 1.5 the effect is increase the apparent range by 50% which darkens all colors values. [-l <f_lowerFilter>] [--lowerFilter <f_lowerFilter>] Filter all z-scores below (normalized) <lowerFilter> to 0.0. [-u <f_upperFilter>] [--upperFilter <f_upperFilter>] Filter all z-scores above (normalized) <upperFilter> to 0.0. [-z <zFile>] [--zFile <zFile>] z-score file to read (relative to input directory). Defaults to 'zfile.csv'. [--version] If specified, print version number. [--man] If specified, print (this) man page. [--meta] If specified, print plugin meta data.