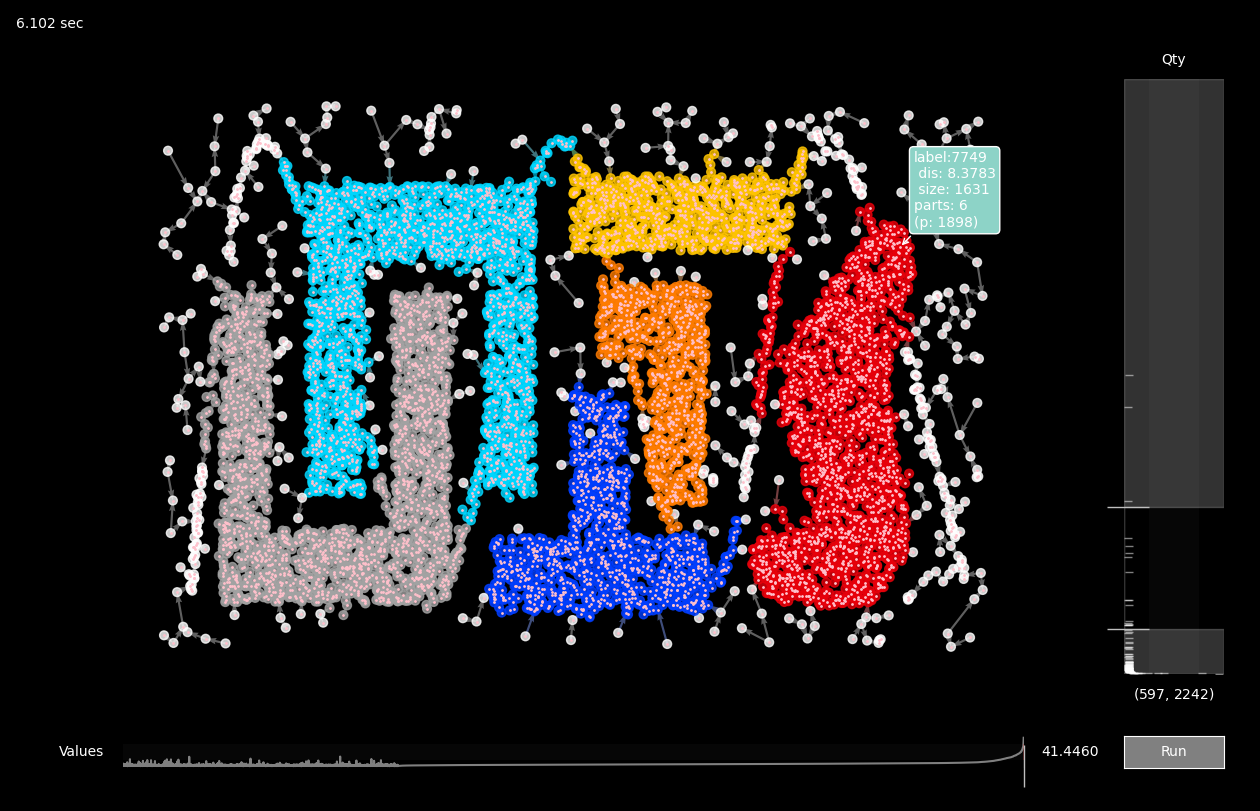
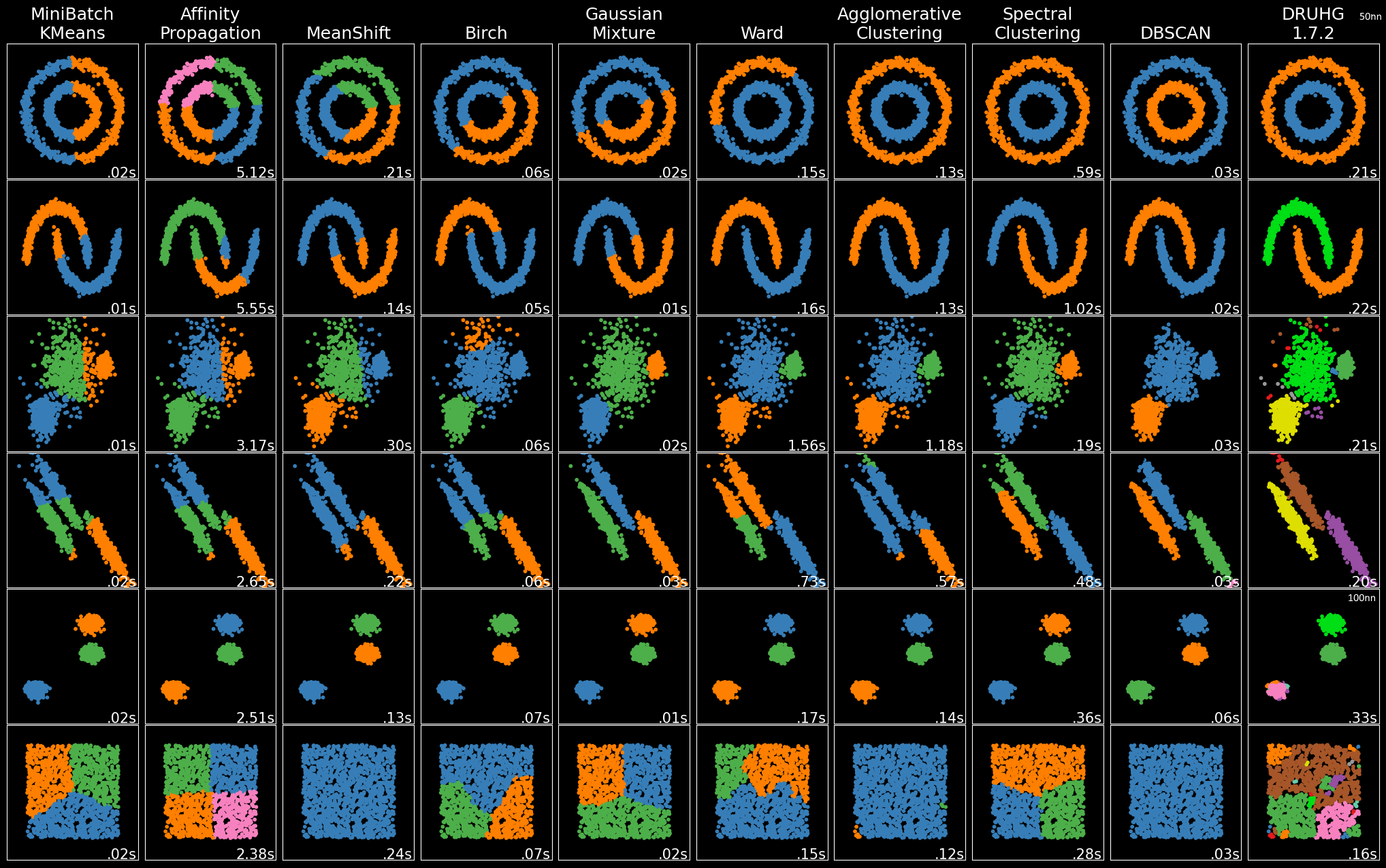
size_range, for genuine result and genuine outliers set to [1,1].fix_outliers allows to label outliers to their closest clusters via mstree edges.max_ranking controls precision vs productivity balance, after some value the precision and the result would not change.algorithm can be set to 'slow' to further enhance the precision.import sklearn.datasets as datasets
import druhg
iris = datasets.load_iris()
XX = iris['data']
clusterer = druhg.DRUHG(max_ranking=50)
labels = clusterer.fit(XX).labels_It will build the tree and label the points. Now you can manipulate clusters by relabeling.
labels = dr.relabel(exclude=[7749, 100], size_range==[0.2, 2242], fix_outliers=1)
ari = adjusted_rand_score(iris['target'], labels)
print ('iris ari', ari)- Relabeling is cheap.
-
-
excludebreaks clusters by label number, -
size_rangerestricts cluster size by percent or by absolute number, -
fix_outlierscolors outliers by connectivity.
-
clusterer.plot(labels)It will draw mstree with druhg-edges.
clusterer.plot()It will provide interactive sliders for an exploration.
max_ranking that can be used to decrease for a better performance.PyPI install, presuming you have an up to date pip:
pip install druhgThe package tests can be run after installation using the command:
pytest -k "test_name"The tests may fail :-D
The druhg library supports Python 3.
We welcome contributions in any form! Assistance with documentation, particularly expanding tutorials, is always welcome. To contribute please fork the project make your changes and submit a pull request. We will do our best to work through any issues with you and get your code merged into the main branch.
The druhg package is 3-clause BSD licensed.