This repo is outdated and will no longer be maintained.
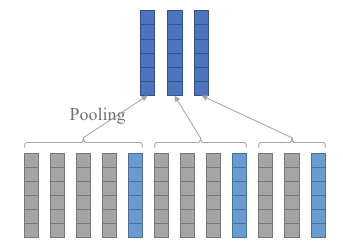
A wrapper layer for splitting and accumulating sequential data.
pip install git+https://github.com/cyberzhg/keras-piecewise.gitimport keras
import keras.backend as K
import numpy as np
from keras_piecewise import Piecewise
class AvePool1D(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(AvePool1D, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def call(self, inputs):
return K.sum(inputs, axis=1) / K.cast(K.shape(inputs)[1], K.floatx())
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (input_shape[0],) + input_shape[2:]
data = [[[1, 3, 2, 5], [7, 9, 2, 3], [0, 1, 7, 2], [4, 7, 2, 5]]]
positions = [[1, 3, 4]]
piece_num = len(positions[0])
data_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=(None, None))
position_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=(piece_num,), dtype='int32')
pool_layer = Piecewise(AvePool1D())([data_input, position_input])
model = keras.models.Model(inputs=[data_input, position_input], outputs=pool_layer)
model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(), loss=keras.losses.mean_squared_error)
model.summary()
print(model.predict([np.asarray(data), np.asarray(positions)]).tolist())
# The result will be:
# [[
# [1.0, 3.0, 2.0, 5.0],
# [3.5, 5.0, 4.5, 2.5],
# [4.0, 7.0, 2.0, 5.0],
# ]]The default value for argument pos_type is Piecewise.POS_TYPE_SEGMENTS, which means splitting the input sequences with increasing positions. When pos_type is Piecewise.POS_TYPE_PAIRS, every two positions represent the piece to be extracted.
import keras
import keras.backend as K
import numpy as np
from keras_piecewise import Piecewise2D
class MaxPool2D(keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(MaxPool2D, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def call(self, inputs):
return K.max(K.max(inputs, axis=1), axis=1)
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return (input_shape[0],) + input_shape[3:]
data = [
[
[1, 3, 5, 2],
[2, 5, 6, 1],
[7, 1, 5, 3],
[7, 2, 2, 4],
],
[
[1, 3, 5, 2],
[2, 5, 6, 1],
[7, 1, 5, 3],
[7, 2, 2, 4],
],
]
rows = [
[2, 4],
[3, 4],
]
cols = [
[1, 2, 4],
[1, 3, 4],
]
row_num = len(rows[0])
col_num = len(cols[0])
data_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=(None, None))
row_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=(row_num,))
col_input = keras.layers.Input(shape=(col_num,))
pool_layer = Piecewise2D(
layer=MaxPool2D(),
)([data_input, row_input, col_input])
model = keras.models.Model(inputs=[data_input, row_input, col_input], outputs=pool_layer)
model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(), loss=keras.losses.mean_squared_error)
model.summary()
print(model.predict([np.asarray(data), np.asarray(rows), np.asarray(cols)]).tolist())
# The result will be:
# [
# [
# [2.0, 5.0, 6.0],
# [7.0, 2.0, 5.0],
# ],
# [
# [7.0, 6.0, 3.0],
# [7.0, 2.0, 4.0],
# ],
# ]