solsim
solsim is the Solana complex systems simulator. It simulates behavior of dynamical systems—DeFi protocols, DAO governance, cryptocurrencies, and more—built on the Solana blockchain.
Philosophy
Define your system how you see fit.
solsim will simulate its behavior and collect its results in a structured, straightforward manner.
Usage
- Implement
initialStepandstepmethods. - From each, return the current state, i.e. a dictionary mapping variables to current values.
- Specify the variables you'd like to "watch."
- Instantiate a Simulation, call .run().
- Receive a pandas DataFrame containing values of "watched" variables at each step in time.
With Solana
from anchorpy import Context
from solana.keypair import Keypair
from solsim.simulation import Simulation
class SomeSolanaSystem(BaseSolanaSystem):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__("path/to/workspace")
self.account = Keypair()
self.pubkey = self.account.public_key
self.program = self.workspace["my_anchor_program"] # solsim gives a Anchor program workspace (self.workspace).
async def initialStep(self):
self.program.rpc["initialize"]() # Make RPC calls to your Anchor program.
await self.client.request_airdrop(self.pubkey, 10) # solsim gives you a Solana API client (self.client).
return {"balance": await self.client.get_balance(self.pubkey)}
async def step(self, state, history):
self.program.rpc["submit_uniswap_trade"](
ctx=Context(accounts={"account": self.pubkey}, signers=[self.account])
)
return {"balance": await self.client.get_balance(self.account)}
simulation = Simulation(system=SomeSolanaSystem(), watchlist=("balance"), n_steps=5)
results = simulation.run() # Returns pandas DataFrame of results.Without Solana
class SomeSystem(BaseSystem):
def __init__(self, population):
self.pop = population
def initialStep(self):
return {"population": self.pop}
def step(self, state, history):
return {"population": state["population"] * 1.1}
simulation = Simulation(system=SomeSystem(), watchlist=("population"), n_steps=5)
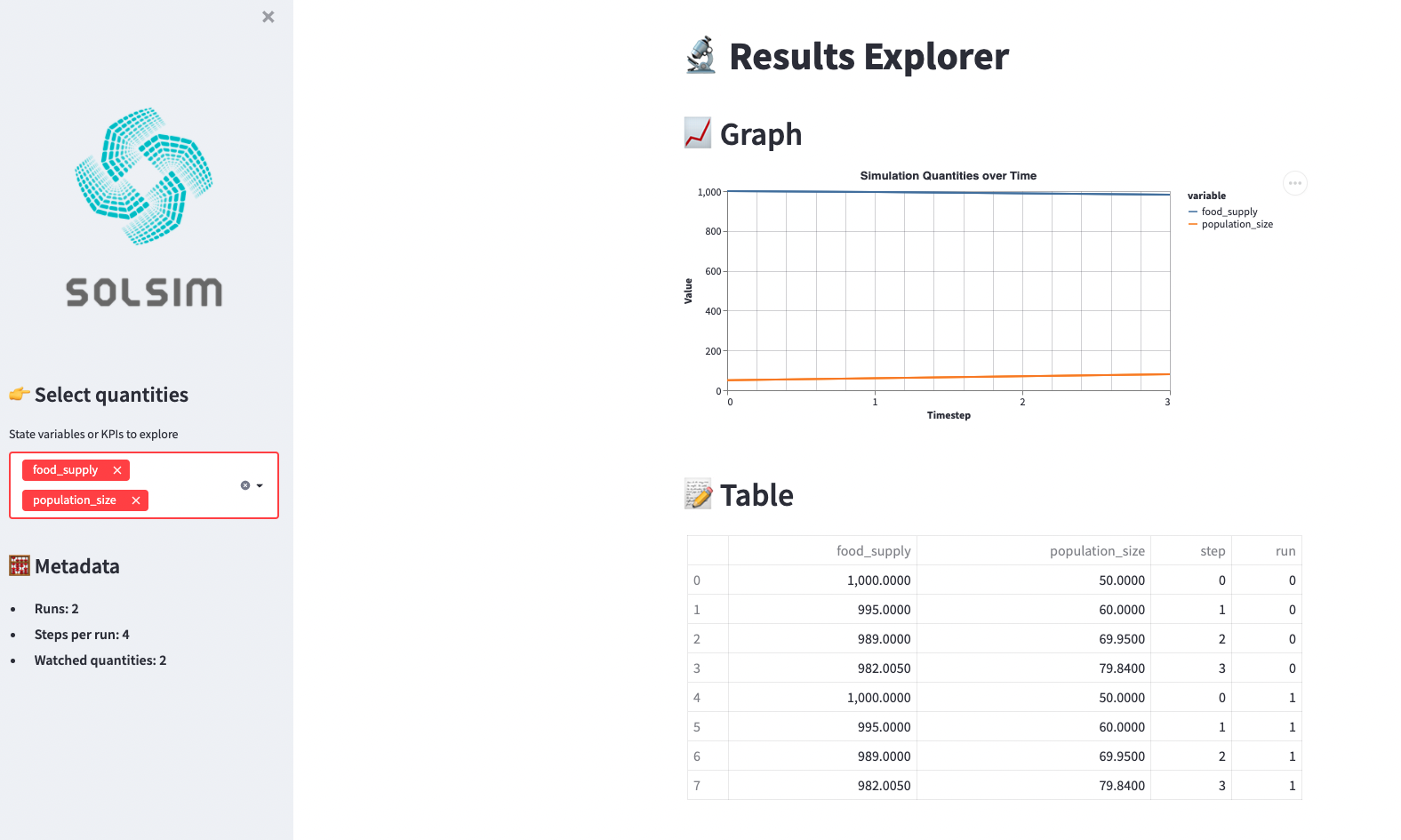
results = simulation.run()Results Explorer
solsim gives you a streamlit app to explore results, e.g.
Installation
First, install Anchor.
Library
pip install solsimDevelopment
Install poetry. Then,
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/cavaunpeu/solsim.git
cd solsim
poetry install
poetry shellDetailed Usage
With Solana
First, write your Solana program. solsim prefers you do this in Anchor. Then,
- Write a system class that inherits from
BaseSolanaSystem. - Call
super().__init__("path/to/program")in its__init__. - Implement
initialStepandstepmethods. (Since you'll interact with Solana asynchronously, these methods should beasync.)
In 2., solsim exposes the following attributes to your system instance:
-
self.workspace: IDL clients for the Solana programs that comprise your system (via anchorpy).
For example, these clients let you interact with your respective programs' RPC endpoints.
-
self.client: a general Solana client (via solana-py).
This client lets you interact with Solana's RPC endpoints. Documentation here.
Finally,
- Define a
watchlist: variables (returned ininitialStepandstep) you'd like to "watch." - Instantiate and run your simulation, e.g.
Simulation(MySystem(), watchlist, n_steps=10).run().
Without Solana
- Write a system class that inherits from
BaseSystem. - Implement
initialStepandstepmethods. - Define a
watchlist. - Instantiate and run your simulation.
Examples
Drunken Escrow
Agents are randomly paired to exchange random amounts of foo_coin and bar_coin via an Anchor escrow contract in each timestep.
- Run:
python -m examples.drunken_escrow. - Code: here.
- Expected output (numbers may vary):
(.venv) ➜ solsim git:(main) $ python -m examples.drunken_escrow
Waiting for Solana localnet cluster to start (~10s) ...
Steps completed: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 4/4 [00:27<00:00, 6.82s/it]
step mean_balance_spread mean_swap_amount num_swaps
0 -1 40.000000 30.666667 3
1 0 58.000000 12.000000 3
2 1 60.666667 4.000000 3
3 2 83.333333 21.500000 2
Lotka-Volterra
The Lotka-Volterra model is a classic dynamical system in the field of ecology that tracks the evolution of interdependent predator and prey populations.
- Run:
python -m examples.lotka_volterra. - Code: here.
- Expected output:
(.venv) ➜ solsim git:(main) ✗ python -m examples.lotka_volterra
Steps completed: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 4/4 [00:00<00:00, 28581.29it/s]
step food_supply population_size
0 -1 1000.000 50.00
1 0 995.000 60.00
2 1 989.000 69.95
3 2 982.005 79.84
This implementation inspired by cadCAD Edu.
Inspiration
solsim humbly builds on the shoulders of the giants that are cadCAD and tokenspice, among others.